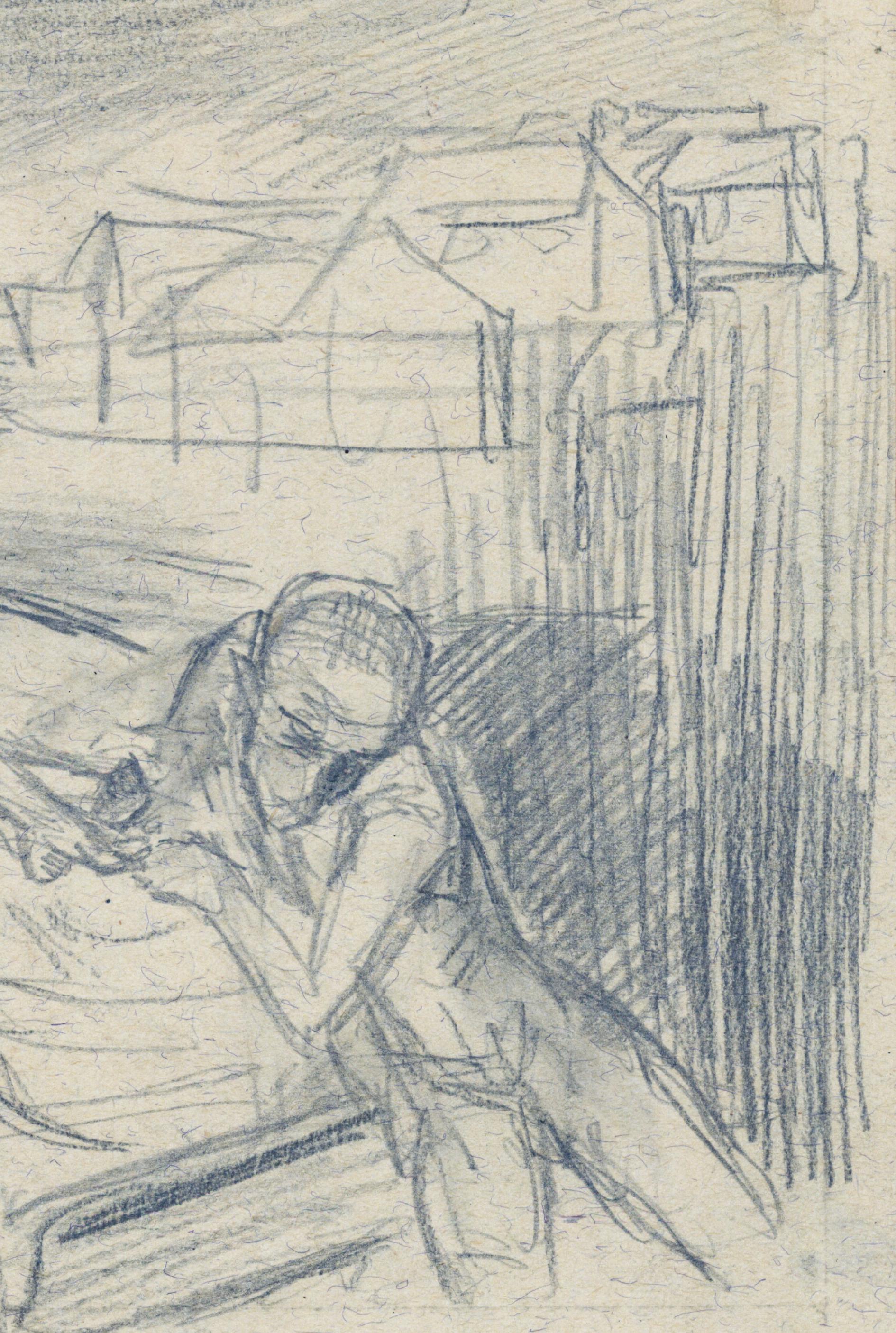
Was Drogobych the Capital of the 20th Century?
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26881/sf.2018.11.01Keywords:
Bruno Schulz, Drohobycz, stereotype, center-periphery, Georg SimmelAbstract
Nowadays it is impossible to think about Schulz outside Drogobych. Wherever else he showed up, be it Vienna, Marienbad, Kudowa, Zakopane, Warsaw or Paris, he was a refugee, a patient, a visitor or a tourist – always a stranger. And he considered himself one, while others did the same. To an extent, it was his own fault. It could perhaps be otherwise if he did not so often write in his letters (and most likely said in conversations) that he was unable to live and work outside his hometown. But the words of the writer could only encourage others to contribute to a stereotype of a “modest schoolteacher from a small town.” The provincial status of Schulz, however, is not so obvious. At the end of the 19th century, thanks to oil Drogobych reached the end of centuries long stasis from which even the salt mines opened in the Middle Ages could not save it. Oil changed the life of many people in Galicia. Without leaving Drogobych, Schulz could actually watch and personally experience in doses which let him keep his independence and inner stability the rise of a metropolitan mentality described by Georg Simmel. Yet Paris was too much for him – after three weeks he escaped from the French capital with not a single word of commentary. To live in the capital of the 19th century, as Walter Benjamin called it, would have been a torture for him. Thus Schulz did not cancel the opposition of center and periphery, the capital and the provinces, but turned such distinctions upside down. Thanks to writing, the center of the world moved to his hometown so that perhaps Drogobych became the capital of the 20th century.
 Academic Scientific Journals
Academic Scientific Journals





